How images are indexed by Google
Google's web crawler with user agent Googlebot-Image/1.0 discovers and indexes images. The crawling process is out of your direct control but understanding how it works can help you ensure your images are properly indexed.
Here’s how indexing works:
- Embed - add the image to your web page using img src, srcset or as a Sirv responsive image.
- Discover - Google’s crawler discovers your image the next time it visits your HTML page. The crawler parses the entire page like a normal web browser would, including scripts, so it will find all the images, including those requested by Sirv JS.
- Fetch - the crawler requests the image from Sirv and Sirv's nearest CDN server will return it. Sirv CDN ensures images are optimised and returned quickly, which helps your SEO.
- Analyze and index - after receiving the image, Google indexes it. To understand the image, Google considers multiple factors including: the text surrounding the image on your page (this gives it context); the image alt text; and the image file name. Google saves this information in its index and uses it to help determine where images will rank in search results.
Check your images in Google's index
There are two ways to check if your images have been indexed by Google.
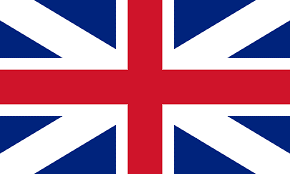
Perform a search in Google Images to look for site:https://example.com/my-page.html (enter the actual URL of the page you want to check). The search results will display the images that Google has indexed for that page. It looks like this:
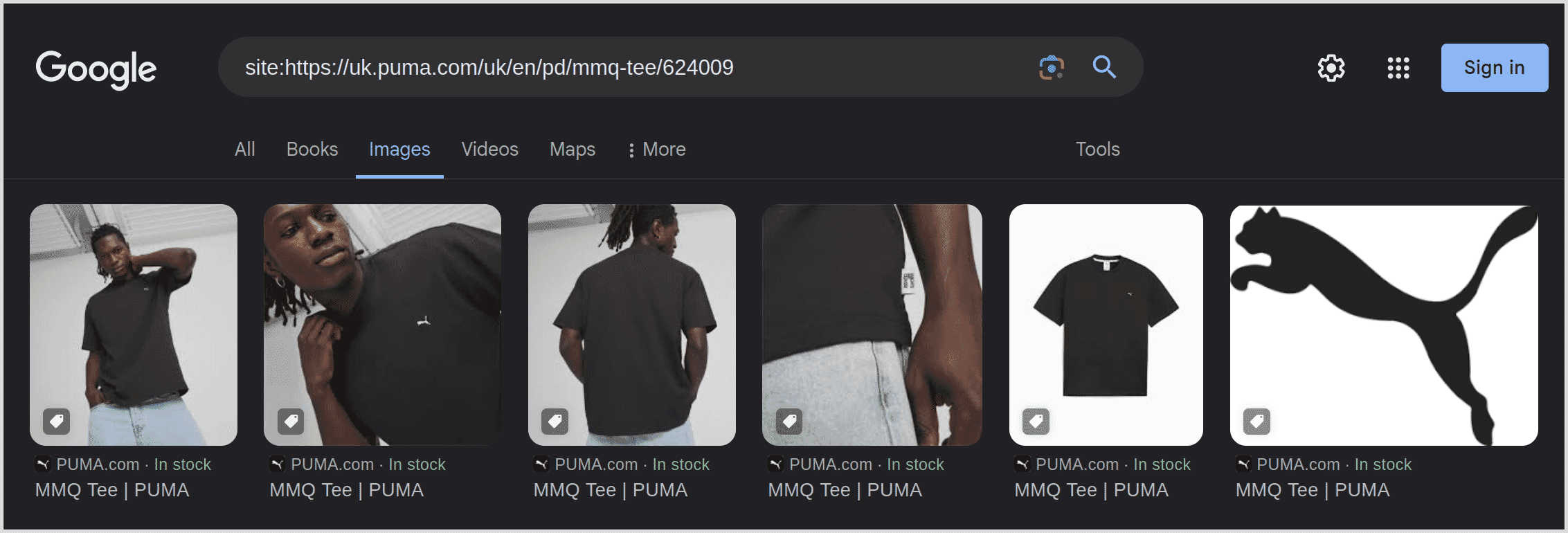
Alternatively, use Google's Rich Results Test to check if a specific image has been indexed. Paste the image URL into the search box, then look at the "Crawl" details. It will state if and when the image was successfully crawled:
Why images may not be indexed
There are several reasons why images may not be indexed by Google:
- Noindex tag - if the page containing the image has a noindex tag, Google will not index any content on that page, including images.
- Robots.txt restrictions - if your robots.txt file disallows crawling pages where Sirv images are published, Google won’t index those images.
- Low-quality content - pages with thin or low-quality content may be deemed less valuable by Google and thus may not be indexed.
- Slow loading time - Google's bot will abort (timeout) reading your page if it is taking too long to load and parse the files. This can happen if the HTML file itself is slow but more likely your page has a large number of JavaScripts blocking Sirv JS from requesting images.
"Other error" for images in Google Search Console
If you use the Google Search Console, you might see an "Other error" when you review your web pages:
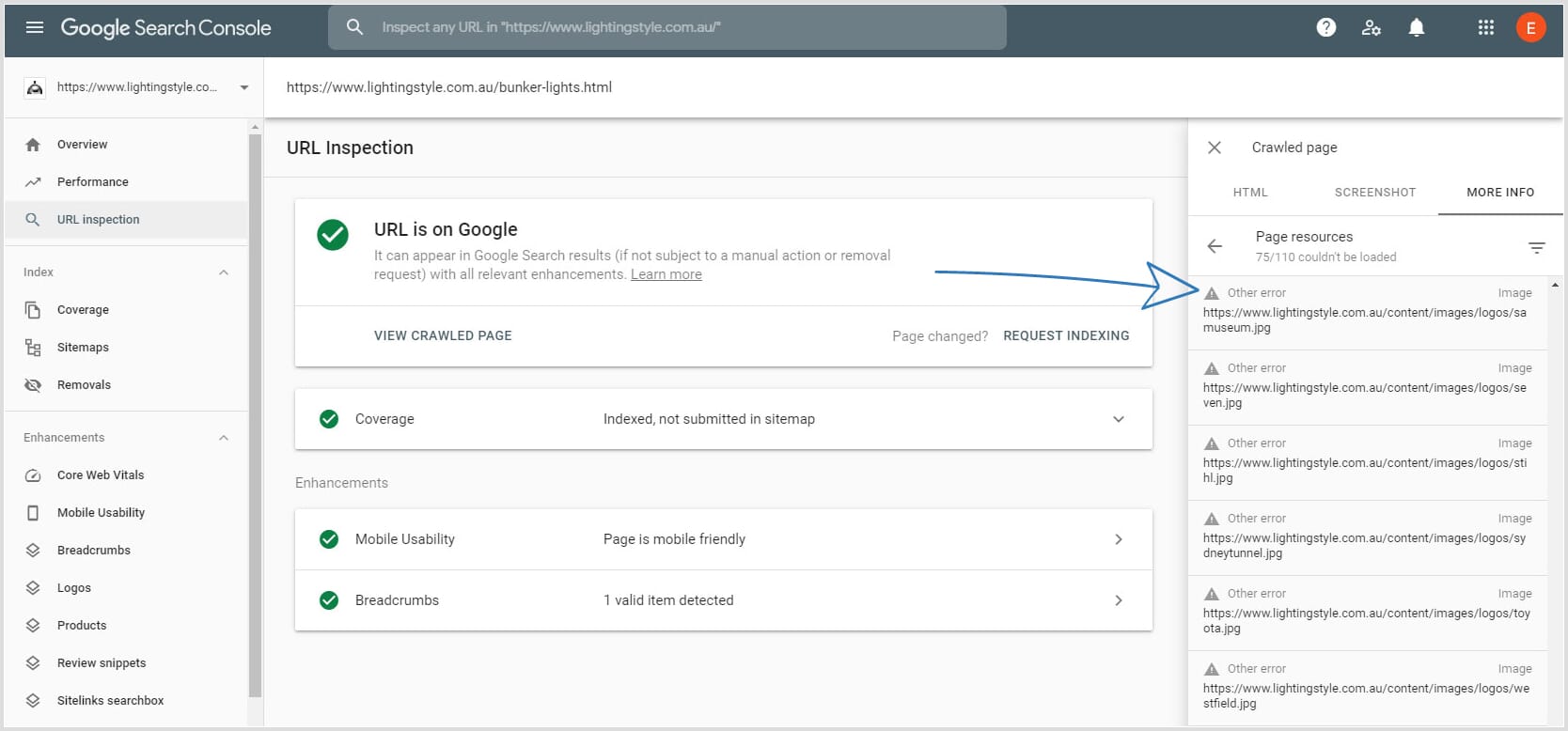
That error happens when its bot Google-InspectionTool skips parts of your web page which it thinks are irrelevant. You will often see a large number of scripts, images and other files in that list. That's okay because Google Search Console is not responsible for image indexing. It provides valuable insights about your page visibility but when it comes to images, what matters is that they are showing in search results.
The important bot is Googlebot-Image/1.0, which is responsible for indexing images. That bot will not skip your page's images and you should see them in Google Image Search, if you check it.
Ask us about image search
If you have any questions about how image indexing works or you want to improve your image search results, please send a message to the Sirv support team.